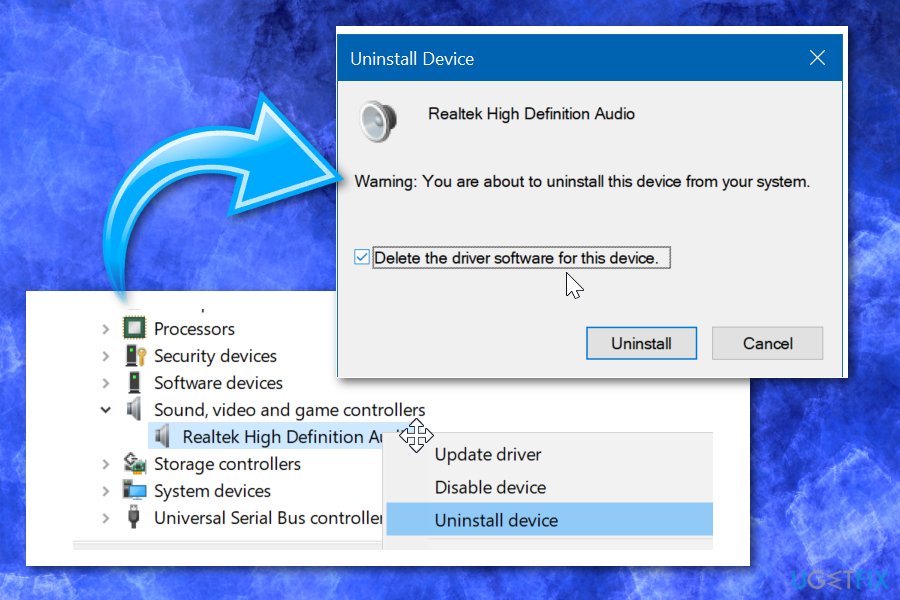
Once installed, you should be able to run gpedit.msc. Click your Windows key + S and search will come up. Type in gpedit.msc. We were not able to test this on Windows 7 but Windows 7 x64 Users should copy the GroupPolicy, GroupPolicyUsers folder, and the gpedit.msc file into the System32 folder from the SysWOW64 folder. Driver Install Tool Linux (rpm) / Linux (deb) Driver Deployment Wizard Win10 / Win10 x64 / Win8.1 / Win8.1 x64 / Win8 / Win8 x64 / 2019 / 2016 / 2012 R2 / 2012. Type devmgmt.msc and then Enter. Click on View and then Show hidden Devices. Now check if the driver exists. Method 2: Windows Update helps keep your computer up to date with the latest system updates and drivers. You can check Windows Update manually to help ensure you have the latest updates.
- Msc Driver Download 64-bit
- Mac Driver Download
- Msc Driver Download Windows 7
- Mc Driver Download
- Msc Driver Download App
- Msc Driver Download Software
Driver Verifier monitors Windows kernel-mode drivers and graphics drivers to detect illegal function calls or actions that might corrupt the system. Driver Verifier can subject Windows drivers to a variety of stresses and tests to find improper behavior. You can configure which tests to run, which allows you to put a driver through heavy stress loads or through more streamlined testing. You can also run Driver Verifier on multiple drivers simultaneously, or on one driver at a time.
Caution
- Running Driver Verifier could cause the computer to crash.
- You should only run Driver Verifier on computers that you are using for testing and debugging.
- You must be in the Administrators group on the computer to use Driver Verifier.
- Driver Verifier is not included in Windows 10 S, so we recommend testing driver behavior on Windows 10 instead.
Where can I download Driver Verifier?
You don't need to download Driver Verifier, because it is included with most versions of Windows in %WinDir%system32 as Verifier.exe. (Driver Verifier is not included with Windows 10 S.) Driver Verifier is not distributed separately as a download package.
For information about changes in Driver Verifier for Windows 10 and previous versions of Windows, see Driver Verifier: What's New.
When to use Driver Verifier
Run Driver Verifier throughout development and testing of your driver. More specifically, use Driver Verifier for the following purposes:
To find problems early in the development cycle, when they are easier and less costly to correct.
For troubleshooting and debugging test failures and computer crashes.
To monitor behavior when you deploy a driver for testing using the WDK, Visual Studio, and the tests from the Windows Hardware Lab Kit (Windows HLK) or Windows Hardware Certification Kit (for Windows 8.1). For more information about testing drivers, see Testing a Driver.
How to start Driver Verifier
You should only run Driver Verifier on test computers, or on computers that you are testing and debugging. To get the most benefit from Driver Verifier, you should use a kernel debugger and connect to the test computer. For more information about debugging tools, see Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg, KD, CDB, NTSD).
Start a Command Prompt window by selecting Run as administrator, and type verifier to open Driver Verifier Manager.
Select Create standard settings (the default task), and select Next.
You can also choose Create custom settings to select from predefined settings, or to select individual options. For more information, see Driver Verifier options and rule classes and Selecting Driver Verifier Options.
Under Select what drivers to verify, choose one of the selection schemes described in the following table.
Option Recommended use Automatically select unsigned drivers Useful for testing on computers that are running versions of Windows that do not require signed drivers.
Automatically select drivers built for older versions of Windows Useful for testing driver compatibility with newer versions of Windows.
Automatically select all drivers installed on this computer Provides maximum coverage in terms of the number of drivers that are tested on a system. This option is useful for test scenarios where a driver can interact with other devices or drivers on a system.
This option can also exhaust the resources available for Special Pool and some resource tracking. Testing all drivers can also adversely affect system performance.
Select driver names from a list In most cases, you will want to specify which drivers to test.
Selecting all drivers in a device stack allows the Enhanced I/O Verification option to track objects and check compliance because an I/O request packet (IRP) is passed between each of the drivers in the stack, which allows for a greater level of detail to be provided when an error is detected.
Select a single driver if you are running a test scenario that measures system or driver performance metrics, or if you want to allocate the greatest number of resources available for detecting memory corruption or resource tracking issues (such as deadlocks or mutexes). The Special Pool and I/O Verification options are more effective when used on one driver at a time.
If you chose Select driver names from a list, select Next, and then select one or more specific drivers.
Select Finish, and then restart the computer.
Note
You can also run Driver Verifier in a Command Prompt window without starting Driver Verifier Manager. For example, to run Driver Verifier with the standard settings on a driver called myDriver.sys, you would use the following command:
For more information about command line options, see Driver Verifier Command Syntax.
How to control Driver Verifier
You can use either Driver Verifier Manager or a command line to control Driver Verifier. To start Driver Verifier Manager, see How to start Driver Verifier, earlier in this topic.
For each of the following actions, you can use Driver Verifier Manager or enter a command line.
To stop or reset Driver Verifier
Msc Driver Download 64-bit
In Driver Verifier Manager, select Delete existing settings, and then select Finish.
or
Enter the following command at a command prompt:
Restart the computer.
To view Driver Verifier statistics
In Driver Verifier Manager, select Display information about the currently verified drivers, and then select Next. Continuing to select Next displays additional information.
or
Enter the following command at a command prompt:
To view Driver Verifier settings
In Driver Verifier Manager, select Display existing settings, and then select Next.
or
Enter the following command at a command prompt:
Mac Driver Download
How to debug Driver Verifier violations
To get the most benefit from Driver Verifier, you should use a kernel debugger and connect it to the test computer. For an overview of debugging tools for Windows, see Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg, KD, CDB, NTSD).
If Driver Verifier detects a violation, it generates a bug check to stop the computer. This is to provide you with the most information possible for debugging the issue. When you have a kernel debugger connected to a test computer that is running Driver Verifier, and Driver Verifier detects a violation, Windows breaks into the debugger and displays a brief description of the error.
All violations detected by Driver Verifier result in bug checks. Common bug check codes include the following:
For more information, see Handling a Bug Check When Driver Verifier is Enabled. For tips about debugging Bug Check 0xC4, see Debugging Bug Check 0xC4: DRIVER_VERIFIER_DETECTED_VIOLATION.
When you start a new debugging session, use the debugger extension command, !analyze. In kernel mode, the !analyze command displays information about the most recent bug check. To display additional information, to help identify the faulting driver, add option -v to the command at the kd> prompt:
In addition to !analyze, you can enter the following debugger extensions at the kd> prompt to view information that is specific to Driver Verifier:
!verifier dumps captured Driver Verifier statistics. Use !verifier -? to display all of the available options.
!deadlock displays information related to locks or objects tracked by Driver Verifier's deadlock detection feature. Use !deadlock -? to display all of the available options.
!iovirp [address] displays information related to an IRP tracked by I/O Verifier. For example:
!ruleinfo [RuleID] displays information related to the DDI compliance checking rule that was violated. (RuleID is always the first argument to the bug check.) All rule IDs from DDI compliance checking are in the form 0x200nn. For example:
Related topics
Sometimes Windows system displays error messages regarding corrupted or missing services.msc files. Situations like that can occur, for example, during a software installation process. Each software program requires certain resources, libraries, and source data to work properly. Corrupted or nonexistent services.msc file can therefore effect in failed execution of the started process.
services.msc file Microsoft Management Console Snap-in. The file was developed by Microsoft for use with Windows software. Here you will find detailed information about the file and instructions how to proceed in the event of services.msc related errors on your device. You can also download services.msc file compatible with Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows XP, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows Vista devices which will (most probably) allow you to solve the problem.
Compatible with: Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows XP, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows VistaUser popularityFix services.msc errors
File info
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Filename | services.msc |
| File extension | MSC |
| Type | Executable Application |
| Description | Microsoft Management Console Snap-in |
Msc Driver Download Windows 7
| Software | |
|---|---|
| Program | Windows 10 |
| Software | Windows |
| Author | Microsoft |
| Software version | 10 |
| Details | |
|---|---|
| File size | 92746 |
| Oldest file | 2006-09-18 |
| MIME type | application/xml |
Most common services.msc file related problems
There are various types of errors related to services.msc file. services.msc file may be located in wrong file directory on your device, may not be present in the system, or may be infected with malicious software and therefore not work correctly. Below is a list of most common error messages related to services.msc file. If you encounter one listed below (or similar), please consider the following suggestions.
- services.msc is corrupted
- services.msc cannot be located
- Runtime Error - services.msc
- services.msc file error
- services.msc file cannot be loaded. Module was not found
- cannot register services.msc file:
- services.msc file could not be loaded
- services.msc file doesn't exist
services.msc
Application could not be started because services.msc file is missing. Reinstall the application to solve the problem.
Problems related to services.msc can be addressed in various ways. Some methods are meant only for advanced users. If you don't have confidence in your skills, we suggest consulting a specialist. Fixing services.msc file errors should be approached with utmost caution for any mistakes can result in unstable or unproperly working system. If you have the necassary skills, please proceed.
How to fix services.msc errors in just few steps?
services.msc file errors can be caused by various factors, so its is beneficial to try to fix them using various methods.
Step 1: Scan your computer for any malicious software
Windows files are commonly attacked by malicious software that prevents them from working properly. First step in addressing problems with services.msc file or any other Windows system files should be scanning the system for malicious software using an antivirus tool.
If by any chance you don't have any antivirus software installed on your system yet, you should do it immediately. Unprotected system is not only a source of file errors, but, more importantly, makes your system vulnerable to many dangers. If you don't know which antivirus tool to choose, consult this Wikipedia article – comparison of antivirus software.
Step 2: Update your system and drivers.
Installing relevant Microsoft Windows patches and updates may solve your problems related to services.msc file. Use dedicated Windows tool to perform the update.

- Go to the Windows 'Start' menu
- Type 'Windows Update' in the search field
- Choose the appropriate software program (name may vary depending on your system version)
- Check if your system is up to date. If any unapplied updates are listed, install them immediately.
- After the update has been done,restart your computer in order to complete the process.
Beside updating the system, it is recommended that you install latest device drivers, as drivers can influence proper working of services.msc or other system files. In order to do so, go to your computer or device producer's website where you will find information regarding latest driver updates.
Step 3: Use System File Checker (SFC) tool

System File Checker is a Microsoft Windows tool. As the name suggests, the tool is used for identyfing and addressing system file related errors, including those related to services.msc file. After an error related to%fileextension% file has been discovered, the program attempts to automatically replace the services.msc file with properly working version. To use the tool:
- Go to the Windows 'Start' menu
- Type 'cmd' in the search field
- Locate 'Command Prompt' result – don't run it yet:
- Click the right mouse button and select 'Run as Administrator' option
- Type 'sfc /scannow' in console prompt to start the program and follow the instructions
Step 4: Restoring Windows system
Another approach is to restore system to previous state, before the services.msc file error occured. In order to restore your system, follow the instructions below
- Go to the Windows 'Start' menu
- Type 'System Restore' in the search field
- Start the system restore tool – it's name may differ depending on version of the system
- The application will guide you through the process – read the messages carefully
- After the process has finished, restart your computer.
If all the above-mentioned methods failed and the services.msc file problem has not been resolved, proceed to the next step. Remember that the following steps are intended only for advanced users.
Download and replace services.msc file
The last solution is to manually download and replace services.msc file in appropriate folder on the disk. Select file version compatible with your operating system and click the 'Download' button. Next, go to your web browser's 'Downloaded' folder and copy the downloaded services.msc file.
Go to the folder where the file should be located and paste the downloaded file. Below is the list of services.msc file example directory paths.
- Windows 10: C:WindowsSystem32
- Windows 7: ---
- Windows XP: ---
- Windows 8.1: ---
- Windows 8: ---
- Windows Vista: ---
If the steps did not solve your services.msc file problem, you should consult a professional. A probability exists that the error(s) might be device-related and therefore should be resolved at the hardware level. A fresh operating system installation might be necessary – a faulty system installation process can result in data loss.
File versions list

| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 2d8d95469ec26aaa986aad1ce424e631 | |
| SHA1 | 67bb8c749cd81b61c96b676525789d49d9bc9506 | |
| SHA256 | eb34e1de291616f983be230fe759324aca5466c79cc393d0b3e80de80914ccef | |
| CRC32 | 2d237854 | |
| Example file location | C:WindowsSystem32 | |
Mc Driver Download
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 7a1d35f59468b8118af5b8e21df78ae2 | |
| SHA1 | 8c861a73b23b92e0cae74aa275c4029bdcf1ec77 | |
| SHA256 | 00d8538999941044286c2ad69600b4c158dbc7a1da6546b49f73327cbb5c3453 | |
| CRC32 | 867796a3 | |
| Example file location | --- | |
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | e8089aa2a6f7fee89b38c1f2d77ba6c6 | |
| SHA1 | 03e9708ef3aa790fe75f7122ea418ae942815005 | |
| SHA256 | 1121f328d1471ee4bd0f625594e69eaa3a8720cf1014c625e9480e4e62301470 | |
| CRC32 | 23fa2b96 | |
| Example file location | --- | |
Msc Driver Download App
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 2d8d95469ec26aaa986aad1ce424e631 | |
| SHA1 | 67bb8c749cd81b61c96b676525789d49d9bc9506 | |
| SHA256 | eb34e1de291616f983be230fe759324aca5466c79cc393d0b3e80de80914ccef | |
| CRC32 | 2d237854 | |
| Example file location | --- | |
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 2d8d95469ec26aaa986aad1ce424e631 | |
| SHA1 | 67bb8c749cd81b61c96b676525789d49d9bc9506 | |
| SHA256 | eb34e1de291616f983be230fe759324aca5466c79cc393d0b3e80de80914ccef | |
| CRC32 | 2d237854 | |
| Example file location | --- | |
Msc Driver Download Software
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 7a1d35f59468b8118af5b8e21df78ae2 | |
| SHA1 | 8c861a73b23b92e0cae74aa275c4029bdcf1ec77 | |
| SHA256 | 00d8538999941044286c2ad69600b4c158dbc7a1da6546b49f73327cbb5c3453 | |
| CRC32 | 867796a3 | |
| Example file location | --- | |
